Filament v4 Beta - Feature Overview
- Introduction
- Latest updates
- General
- Resources
- Navigation
- Schemas
- Forms
- Infolists
- Tables
- Actions
- Widgets
- Dashboard
- Multi-tenancy
- Panel configuration
- Conclusion

#Introduction
The Filament v4 Beta is here with a range of powerful, helpful updates. It's faster, easier to use, and gives you more control when building applications. In this article, we highlight what's new and how these changes can improve your workflow!
To upgrade your app to Filament v4 beta, please read the upgrade guide. To install Filament v4 into a new app, please visit the installation guide.
You are currently viewing the features for Filament
4.x, which is currently inbetaand is notstable. Breaking changes may be introduced to releases during the beta period. Please report any issues you encounter on GitHub.
Looking for the current stable version? Visit the 3.x documentation.
#Latest updates
Updated: June 16, 2025
- Reorderable columns feature in v4.0.0-beta5
#General
#Performance
Rendering and interaction performance in Filament has significantly improved, especially for large tables. Internally, many Blade templates have been optimized to reduce the number of views that are being rendered. By utilizing existing PHP objects to render HTML instead of including new files, Filament v4 reduces the number of files that need to be loaded, improving performance. The size of Blade views has also been reduced by extracting groups of Tailwind CSS classes into dedicated classes, which are then used in the Blade templates. This reduces the amount of HTML that needs to be rendered, resulting in faster page loads and a smaller response size.
#Filament v4 now uses Tailwind CSS v4
Tailwind CSS v4 is a major update focused on performance, flexibility, and modern web standards. It features a reworked configuration system, improved customization, and faster builds, making it easier to build your own custom design system at scale. For the latest features and release notes, visit the Tailwind CSS blog.
Tailwind CSS v4 modernizes its color system by switching from rgb to oklch, using the wider P3 color gamut to produce more vivid, accurate colors beyond the limits of sRGB.
Since Filament v4 is built on Tailwind v4, it also adopts oklch for its theming system.
#Semantic headings and dynamic color systems
With the v4 update, you'll notice a few accessibility features have been implemented throughout your applications:
- Heading levels are now generated dynamically to maintain a proper semantic
HTMLstructure and improve accessibility. - Color palettes are now more accurately generated from a single base color.
- Text colors are dynamically calculated based on the background color of elements to ensure more accessible contrast ratios and to improve readability.
#Authentication
#Multi-factor authentication
Now in Filament v4, in addition to the standard email/password authentication, Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra security step beyond the default email and password login.
Filament supports two built-in MFA methods:
- App authentication using a TOTP app like Google Authenticator, Authy, or Microsoft Authenticator apps.
- Email authentication which sends a one-time code to the user’s email.
Need more MFA options? Additional custom MFA providers can be registered to extend Filament's authentication capabilities.
#Heroicons
Filament includes the Heroicons icon set, so you can use icons without installing anything extra. The new Heroicon enum class provides IDE autocompletion to help you quickly find the icon you need--no more magic strings!
Each icon is available in solid and outlined variants (Heroicon::Star vs. Heroicon::OutlinedStar). Filament automatically selects the appropriate size (16px, 20px, or 24px) based on context.
#Setting a default timezone with FilamentTimezone
The new FilamentTimezone facade lets you set a default timezone for Filament globally via the FilamentTimezone::set() method, simplifying the default timezone across components. This lets you control multiple components at once, including the DateTimePicker, TextColumn, and TextEntry.
#"ISO" formats
Dates and times now support formatting using standard "ISO" formats in the TextColumn and TextEntry components.
#Resources
#Nested resources
Relation managers and relation pages make it easy to display and manage related records within a resource.
For example, in a CourseResource, you might use a relation manager or page to manage the lessons that belong to a course. This lets you create and edit lessons directly from a table using modals.
But if lessons are more complex, modals might not be enough. In that case, you can give lessons their own resource with full-page create and edit views — this is called a nested resource.
#Resource class organization
Resource classes are now generated within their own dedicated namespaces, making your codebase more organized.
#Code quality tips
We have also added some more detailed recommendations on how to keep your Filament code clean and maintainable in v4. Here are a few of our favorites:
- Use schema and table classes to separate large
form()andtable()definitions into their own files. This helps avoid bloated methods and improves readability. - Create dedicated component classes when individual form inputs, table columns, filters, or actions become complex. This keeps each piece of logic focused and reusable.
- Organize components by type and purpose, such as putting form inputs under
Schemas/Componentsand table actions underActions.
#Preserving data when creating another
By default, the Create and create another action clears the form after submission. If you want to retain certain values, you can now use the preserveFormDataWhenCreatingAnother() method on the Create page class and return only the data you want to keep.
When using the Create action, you can use the preserveFormDataWhenCreatingAnother() method.
#Customizing page content
Prior to Filament v4, we didn't have a particularly ergonomic way to customize page layouts in the Filament panel. Now, each page in Filament has its own schema, which defines its structure and content.
You can override the default page schema using the content() method to fully control the layout.
This lets you add, remove, or reorder schema components such as tables, tabs, and custom elements.
#Resource create page redirect
You can now configure the default redirect behavior after creating a resource.
By using the panel configuration, you can choose whether users are redirected to the index page, the view page, or the edit page after creating a record.
This applies globally to all resources within the panel.
#Disabling search term splitting
The new $shouldSplitGlobalSearchTerms property allows you to disable splitting the global search term into individual words, improving search performance on large datasets.
#Relation managers
#Customizing the content tab
The Edit and View pages now support full customization of the main content tab.
By overriding the getContentTabComponent() method, you can use any tab customization options, including changing the label, icon, or even adding custom behaviors.
Previously, only the icon could be customized, but now, the entire tab component is fully configurable.
#Navigation
#Sidebar / Topbar
The Sidebar and Topbar are now Livewire components, allowing them to be updated dynamically.
If you need to refresh them — for example, after a setting or permission change — you can dispatch a refresh-sidebar or refresh-topbar browser event to trigger a reload.
#Schemas
Schemas form the foundation of Filament's Server-Driven UI approach.
They let you build user interfaces in PHP using structured configuration objects—no need to write HTML or JavaScript manually.
These schemas define how your UI looks and behaves, representing components such as forms fields, infolist entries, layout components and prime components.
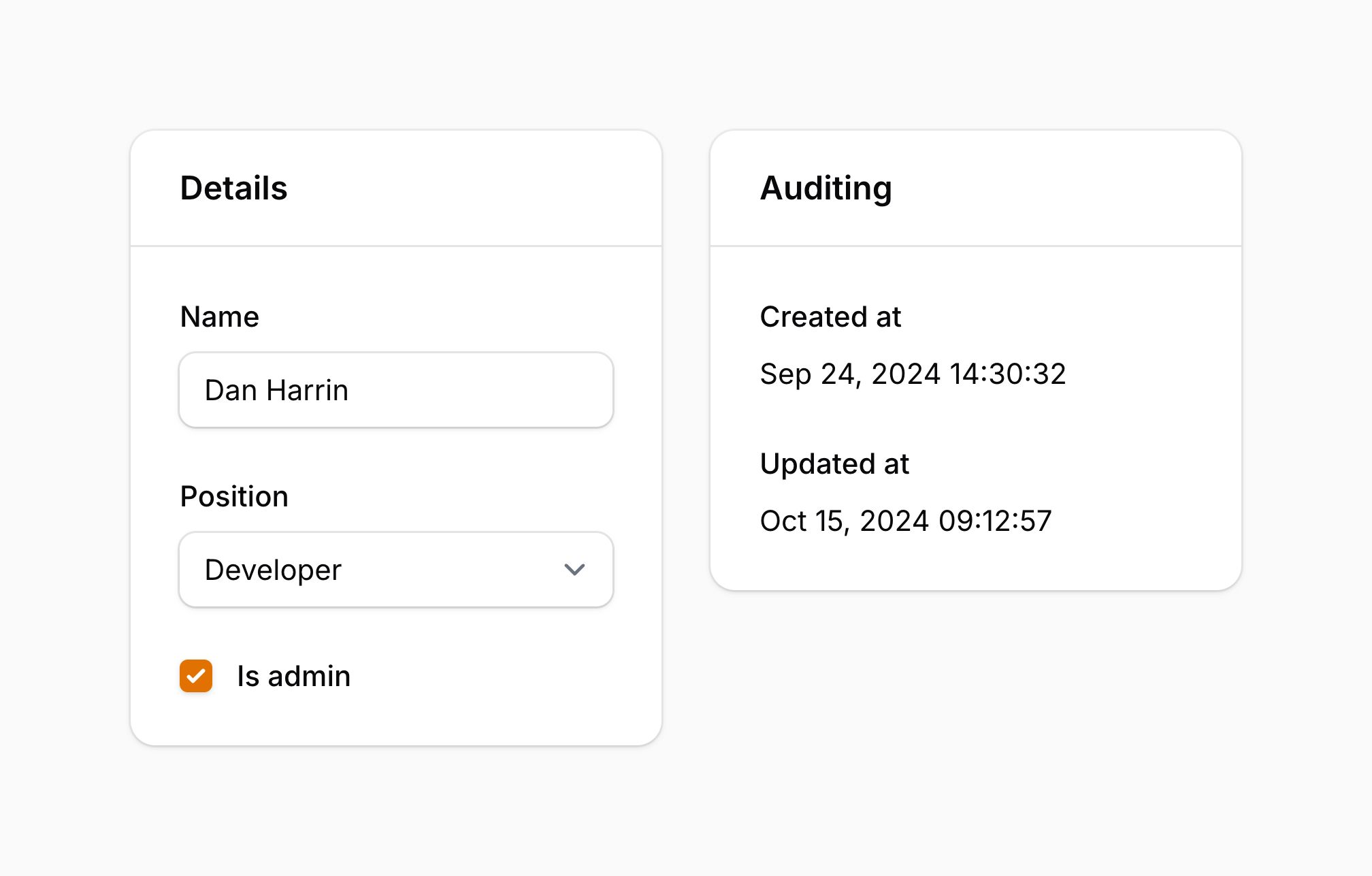
Every Filament UI component — whether it's a form field, a description list, or a static element like text or buttons — is configured through a schema. Components are modular, nestable, and reusable, making your interfaces consistent and easy to maintain.
A schema is represented by a Filament\Schemas\Schema object, and you can pass an array of components to it in the components() method.
For a full list of available components, see the Schemas documentation.
#Vertical tabs
Tabs help organize long or complex schemas by grouping components into separate sections, reducing visual clutter and making forms easier to navigate.
You can now switch to a vertical tab layout by calling the vertical() method.
#Container queries
In addition to traditional breakpoints based on the size of the viewport, you can also use container queries to create responsive layouts based on the size of a parent container.
#Forms
#Rich editor
Rich editor is now using Tiptap, a modern, headless, and highly extensible open source editor framework.
#Storing content as HTML or JSON
By default, the rich editor stores content as HTML. If you would like to store the content as JSON instead, you can use the json() method.
#Custom blocks
Custom blocks are elements that users can drag and drop into the Rich editor.
You can define custom blocks that user can insert into the rich editor using the customBlocks() method.
#Merge tags
Merge tags let users insert "placeholders" — like {{ name }} or {{ today }} — into rich content.
These tags are replaced with dynamic values when the content is rendered, making them useful for things like personalizing messages or displaying dates.
To enable merge tags, use the mergeTags() method when configuring the editor.
Users can insert tags by typing {{ to search, or by using the "merge tags" tool in the toolbar, which opens a panel of available tags for easy insertion.
#Extending the Rich editor
You can extend the Rich editor in Filament by creating custom plugins. These plugins let you add your own TipTap extensions, toolbar buttons, and rendering behavior.
#Slider
The Slider component lets users select one or more numeric values by dragging a handle along a track — ideal for inputs like ranges, ratings, or percentages.

#Code editor
The code editor component lets users write and edit code directly in the interface.
It supports common languages including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, and JSON.
#Table repeaters
Table repeaters display repeater items in a table layout using defined columns.
You can configure these columns with the table() method and TableColumn objects, which map to fields in the repeater's schema.
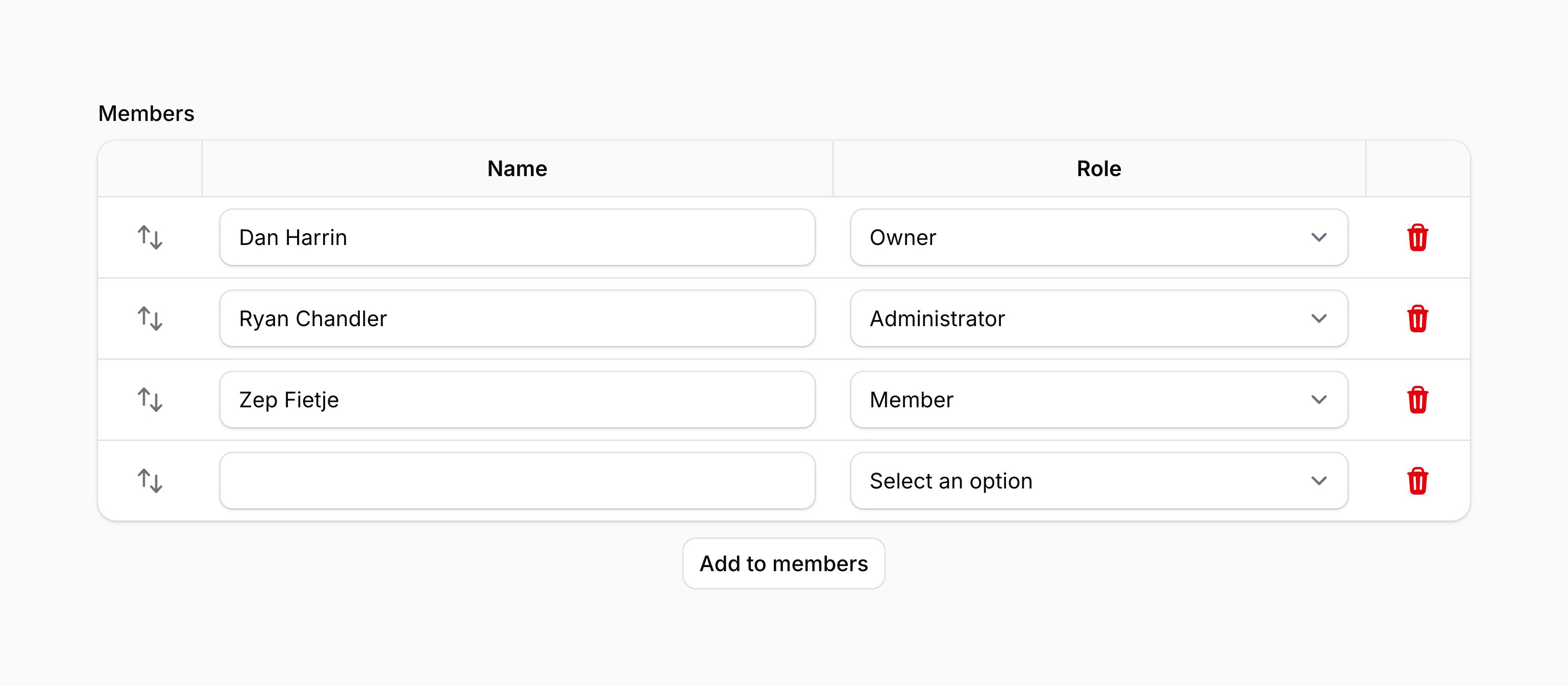
Each column can be customized:
-
hiddenHeaderLabel()hides the label visually but keeps it accessible. -
markAsRequired()adds a red asterisk to indicate required fields. -
wrapHeader()enables line-wrapping for long labels. -
alignment()sets header alignment (start,center, orend). -
width()defines a fixed width for the column.
#Selecting options from a table in a modal
The ModalTableSelect component lets users select records from a modal that displays a full Filament table — ideal for relationships with many records that need advanced search and filtering.
#Using JavaScript to minimise network requests
hiddenJs() and visibleJs()
You can conditionally hide or show fields using the hidden() or visible() methods with a PHP callback.
However, this triggers a full schema reload and a network request whenever the reactive field changes — potentially affecting performance.
For better efficiency, use hiddenJs() or visibleJs() instead. These methods evaluate JavaScript expressions on the client side, allowing you to toggle field visibility instantly without reloading the schema.
#JsContent
You can dynamically set text content — like labels or belowContent() — using JavaScript by passing a JsContent object.
This allows methods like label() and Text::make() to render HTML based on field values.
Inside the JsContent, you can use $state and $get to access the current field's state or other fields in the schema, enabling real-time, reactive text updates without server interaction.
#afterStateUpdatedJs()
When you set the state of another field using $set() inside an afterStateUpdated() function, it modifies the state — but still triggers a network request to reload the schema.
To avoid this, you can use afterStateUpdatedJs(), which runs a JavaScript expression every time the field value changes.
This approach skips the network request entirely and updates fields instantly on the client side.
In this JavaScript context, you can use $state, $get(), and $set() to interact with field states efficiently.
#Fusing fields into a group
The FusedGroup component lets you visually combine multiple fields into a single, compact group.
It's best used with compatible field types like text inputs, selects, date-time pickers and color pickers.
#Adding extra content to a field
Fields contain multiple slots where content can be inserted in a child schema. Slots can accept text, any schema components, actions, or action groups — typically with prime components.
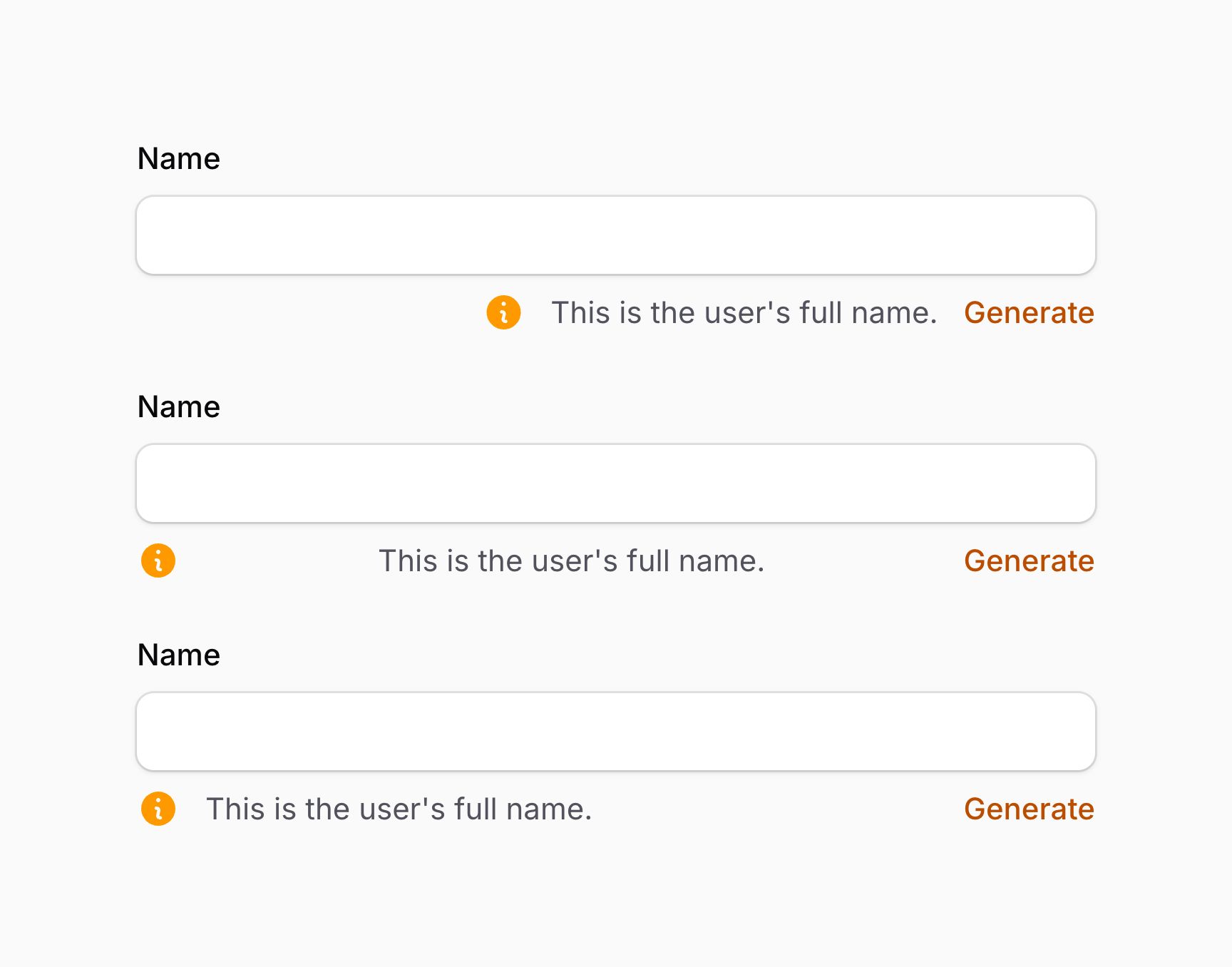
Available slots include:
-
aboveLabel(),beforeLabel(),afterLabel(),belowLabel() -
aboveContent(),beforeContent(),afterContent(),belowContent() -
aboveErrorMessage(),belowErrorMessage()
#Partial rendering
By default, using live() on a field re-renders the entire schema when its value changes.
Filament now offers more efficient options:
-
partiallyRenderComponentsAfterStateUpdated()re-renders only specified fields after state updates. -
partiallyRenderAfterStateUpdated()re-renders just the field itself. -
skipRenderAfterStateUpdated(): prevents any re-rendering, useful when handling logic only.
These tools help optimize field interactions, especially when only part of the form needs to react to changes.
#Improved type casting for form field state
Form field state is now automatically cast to the correct data type. For example, when using a Select field bound to an enum, the state will return an instance of the enum — rather than a raw string—even when accessed via $state or $get().
This improves type consistency and reduces the need for manual casting in your logic.
#Infolists
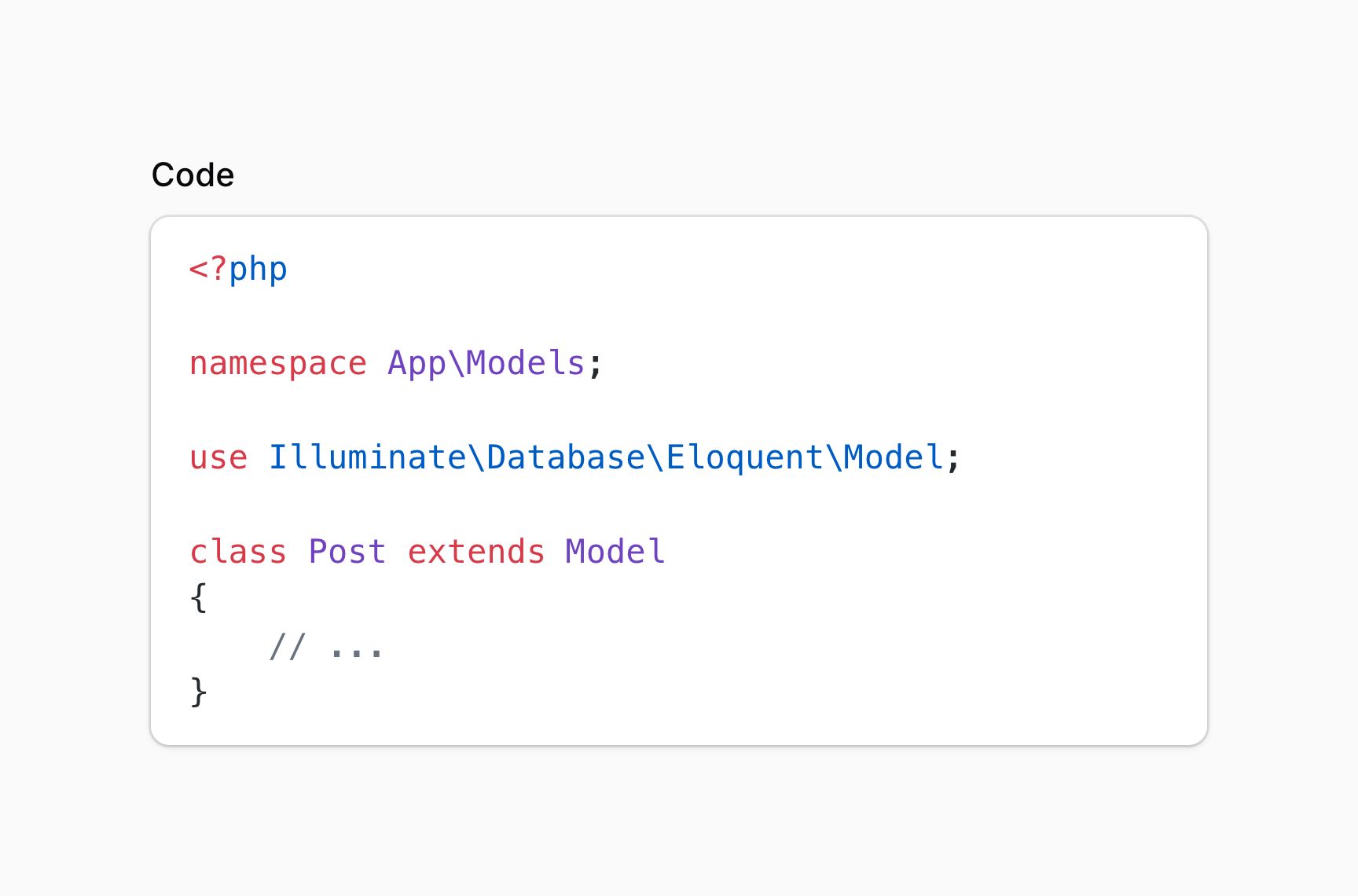
#Code entry
Code entry allows you to present a highlighted code snippet in your infolist. It uses Phiki for code highlighting on the server.
#Tables
#Tables with custom data
Filament tables are typically backed by Eloquent models, but that's not always ideal. When your data isn't stored in a database — or you want to render external or computed data — you can now use custom data as the data source.
To use custom data, pass an array to the records() method. This lets you render simple datasets without a database, while still supporting features like columns, sorting, searching, pagination, and actions.
You can also fetch data from external APIs. For example, use Laravel's HTTP client to pull data from a REST API and return it as an array in records().
This is useful for integrating third-party services or remote backends.
When working with APIs, make sure to implement proper authentication, error handling, and rate limiting.
#Empty relationships with select filters
You can now use the hasEmptyOption() method to include a "None" option that filters for records without a related model. You can customize the label of this option using emptyRelationshipOptionLabel().
#Column headers now visible on empty tables
Table headers are now shown even when no records are present, enhancing the user experience — especially when using column-based search and filters.
#Bulk actions enhancements
See the bulk actions section of this article.
#Reordering Table Columns
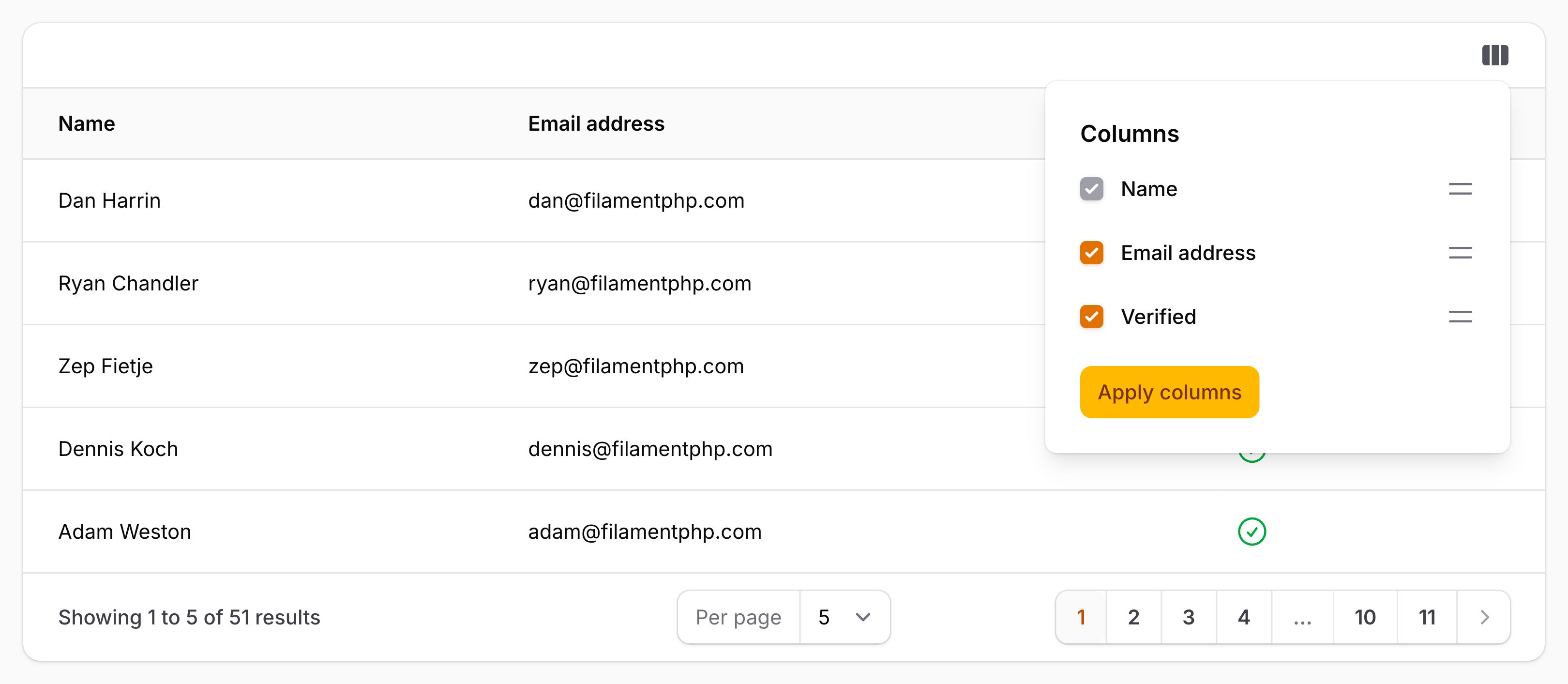
Filament now supports reorderable table columns using the reorderableColumns() method. This allows users to drag and rearrange visible columns for a personalized view.
You can also make the column manager live, so changes apply instantly without needing to click "Apply", by using deferColumnManager(false).
Additionally, the column manager trigger button can be customized via columnManagerTriggerAction(), giving you control over its label, style, and behavior.
#Actions
#Unified actions
Actions are now fully unified across tables, forms, infolists and regular actions.
Instead of having separate Action classes for each context, all actions now use a single Filament\Actions namespace.
#Toolbar actions
Tables now support a dedicated toolbar actions area.
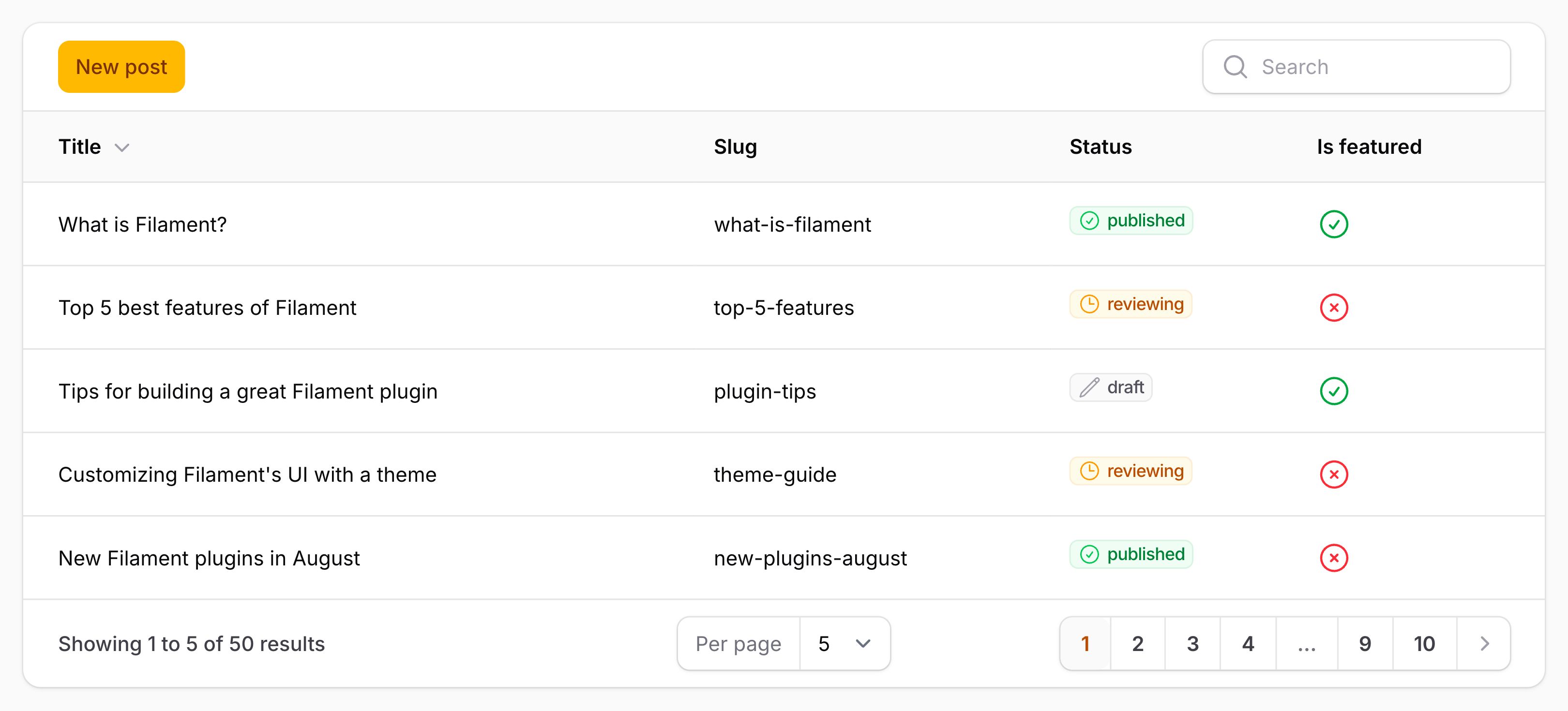
You can place both regular actions and bulk actions in the toolbarActions() method.
This is useful for actions like "create", which are not tied to a specific row, or for making bulk actions more visible and accessible in the table’s toolbar.
#Bulk actions
#Improving bulk action performance
Bulk actions now support the chunkSelectedRecords() method, allowing selected records to be processed in smaller batches instead of loading everything into memory at once — improving performance and reducing memory usage with large datasets.
#Authorizing bulk actions
You can now use authorizeIndividualRecords() to check a policy method for each selected record in a bulk action.
Only the records the user is authorized to act on will be included in the $records array.
#Bulk action notifications
You can now display a notification after a bulk action completes to inform users of the outcome — especially useful when some records are skipped due to authorization.
- Use
successNotificationTitle()when all records are processed successfully. - Use
failureNotificationTitle()to show a message when some or all records fail.
Both methods can accept a function to display the number of successful and failed records using $successCount and $failureCount.
#Prebuilt bulk actions
Prebuilt bulk actions can now run without fetching and hydrating all selected models, significantly boosting performance for large datasets.
#Deselected records
Deselected records are now tracked when using "Select all". This improves performance by minimizing how many record keys need to be stored.
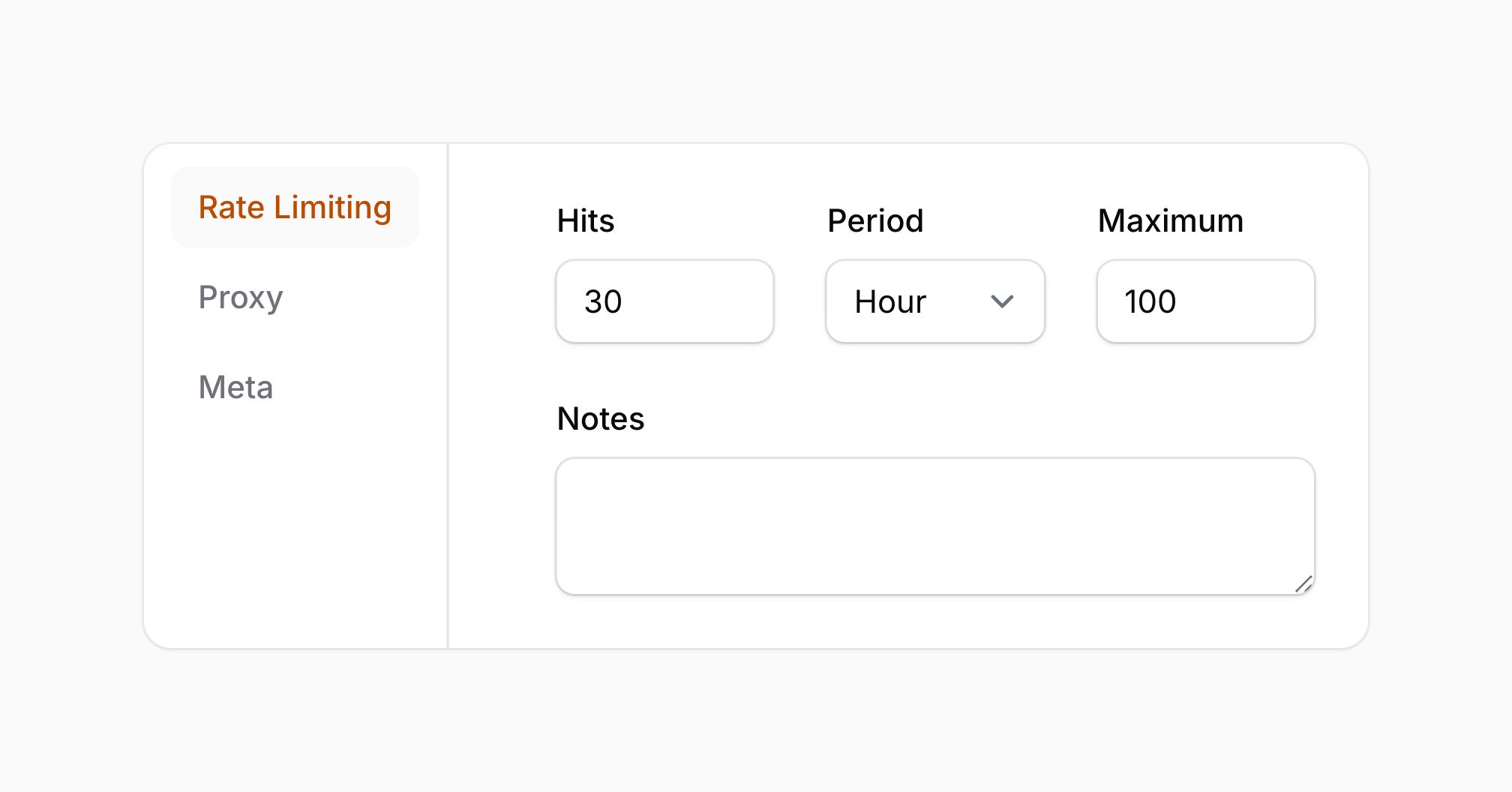
#Rate limiting actions
You can now use the rateLimit() method to limit how often an action can be triggered — per user IP, per minute.
#Authorization
Authorization messages can now be shown in action tooltips and notifications.
#Import action
#Importing relationships
BelongsToMany relationships can now be imported via actions.
#Export action
#Styling XLSX columns
You can now customize the styling of individual cells in XLSX exports using the makeXlsxRow() and makeXlsxHeaderRow() methods in your exporter class.
#Customizing the XLSX writer
You can now configure the OpenSpout XLSX writer in your exporter class:
- Use
getXlsxWriterOptions()to set export options like column widths. - Override
configureXlsxWriterBeforeClosing()to modify the writer instance before it's finalized.
#Tooltips for disabled buttons
You can now display tooltip()s on disabled buttons.
#Testing actions
Testing actions in v4 is now simpler and more streamlined. See the testing actions section for full details.
#Widgets
#Making the chart collapsible
Charts can now be made collapsible by setting the $isCollapsible property to true on the widget class.
#Custom filters for chart widgets
Chart widgets now support custom filter schemas using the HasFiltersSchema trait. You can define filters with filtersSchema() using schema components, and access the submitted filter values via the $this->filters property.
#Dashboard
Dashboard widgets now support the full responsive grid layout system.
#Multi-tenancy
Multi-tenancy now applies global scopes and lifecycle events automatically.
#unique and exists validation
Laravel's default unique and exists validation rules bypass Eloquent models, meaning they ignore global scopes like those used in multi-tenancy. This can lead to false validation failures across tenants.
To ensure proper data isolation between tenants, you can use scopedUnique() and scopedExists() methods.
#Panel configuration
#Inter font now loaded locally
Filament now loads the Inter font locally instead of from a CDN by default. You can change the font using the font() method in the configuration file.
#Sub-navigation position
By default, sub-navigation appears at the start of each page. You can override this globally for the entire panel using the subNavigationPosition() method.
Available options are:
-
Start– default position -
End– renders at the bottom -
Top– displays as tabs
#Strict authorization mode
By default, Filament allows access to a resource if no policy or policy method exists — assuming authorization isn't required.
To enforce stricter security, you can enable strict authorization mode using strictAuthorization().
This will throw an exception if a policy or method is missing, ensuring all access is explicitly defined.
#Email change verification
When using the profile() feature with emailChangeVerification(), users must verify their new email address before it becomes active. A verification link is sent to the new email (valid for 60 minutes), and the address won't update in the database until it's clicked. For added security, a cancellation link is also sent to the user's old email to block unauthorized changes.
#Error notifications
You can now customize how error messages appear in your Filament panel.
When Laravel's debug mode is off, Filament replaces Livewire's full-screen error modals with flash notifications. You can:
- Disable this behavior globally using
errorNotifications(false). - Customize the default error message with
registerErrorNotification(title, body). - Set custom messages for specific HTTP status codes using the
statusCodeparameter. - Enable or disable error notifications on a per-page basis via the
$hasErrorNotificationsproperty.
This gives you full control over the user experience when something goes wrong.
#Conclusion
Filament v4 Beta brings a wide range of improvements designed to make your development experience faster, more consistent, and easier to maintain. Since it's still in beta, now is the perfect time to explore the new features and share feedback.
If you need a stable version, refer to the 3.x documentation.
To upgrade your app to Filament v4 beta, please read the upgrade guide. To install Filament v4 into a new app, please visit the installation guide.
Special thanks to Dan Harrin for his incredible work on Filament v4!
This article was written by Leandro Ferreira, with contributions from André Domingues and reviewed by Dan Harrin and Alex Six.
Leandro is a PHP/Laravel developer who has been coding for close to 7+ years. You can learn more about Leandro on his website.