- Why This Package?
- Features
- Requirements
- Installation
- Quick Start
- Relation Pages
- Advanced Configuration
- Common Patterns
- Troubleshooting
- Testing
- Contributing
- Security
- Credits
- License
A powerful drag-and-drop tree view for Filament resources. Display and manage hierarchical data with the same elegant developer experience you expect from Filament.
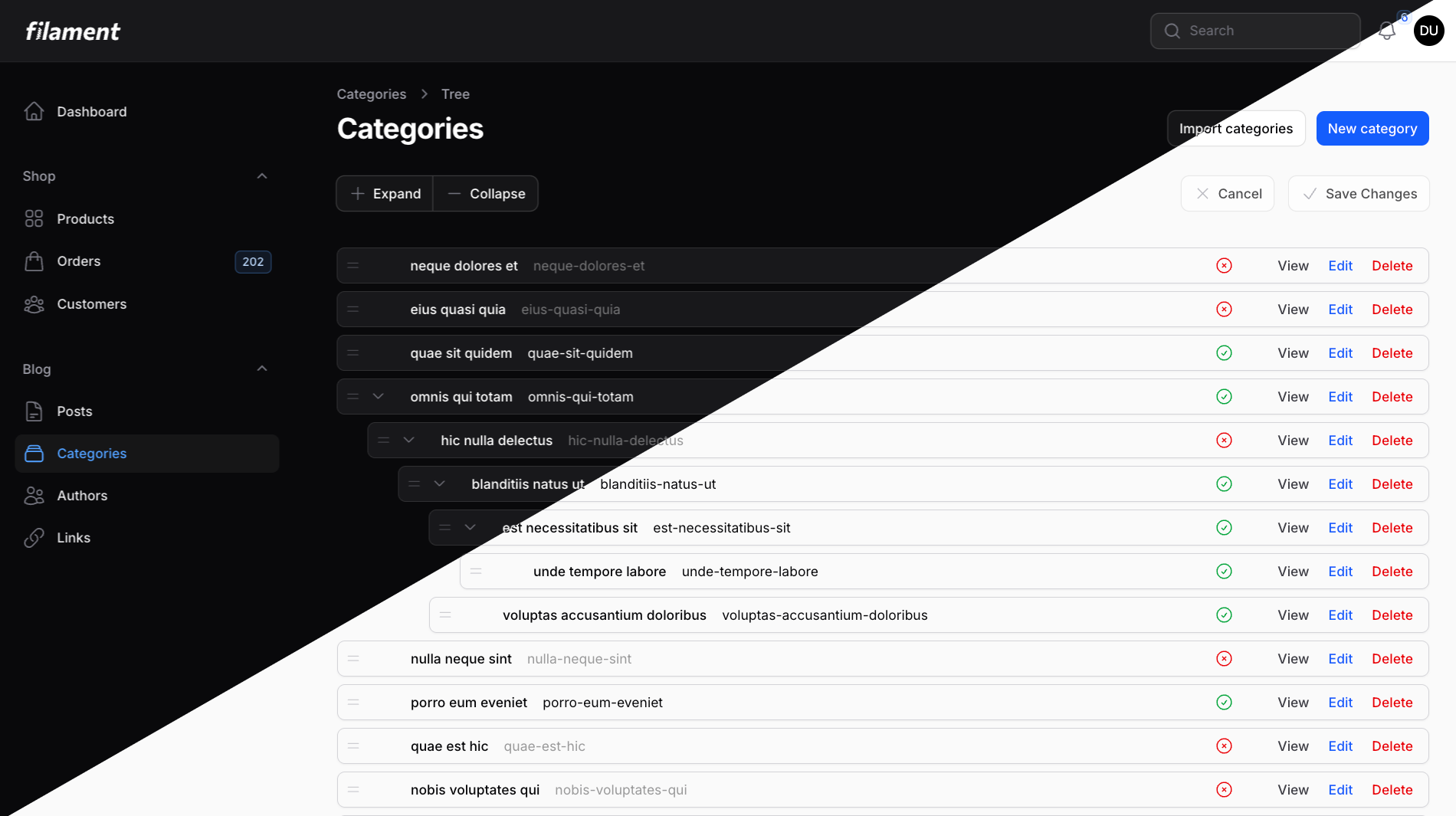
#Why This Package?
We created Filament Tree View because we couldn't find a hierarchical data solution that truly embraced Filament's philosophy and architecture. Most tree packages feel like external additions rather than native Filament components.
Our Goal: Make hierarchical data management feel as natural as using Filament's Table component.
#Built on Proven Technology
Rather than reinventing the wheel, we leverage battle-tested libraries:
- Laravel Adjacency List - Mature, proven package for recursive relationships with thousands of production deployments
- Pragmatic Drag & Drop - Atlassian's accessible, performant drag-and-drop library used in Jira, Trello, and Confluence
- Filament's Core Components - Built with the same patterns, conventions, and architecture as native Filament resources
This foundation gives you reliability, performance, and accessibility out of the box.
#Features
- 🌳 Drag-and-Drop Reordering - Intuitive tree manipulation with visual feedback
- 📦 Drop-in Replacement - Familiar API if you've used Filament Tables
- 🎯 Depth Control - Limit tree nesting to prevent overly complex hierarchies
- 💾 Save Modes - Choose between auto-save or batch save with manual confirmation
- 🎨 Custom Fields - Display any data in your tree nodes with TextField and IconField
- 🔧 Actions Support - Full support for Filament actions (edit, delete, custom actions)
- 🌗 Dark Mode - Seamless integration with Filament's theming system
- ♿ Accessible - Keyboard navigation and screen reader support built-in
- 🔒 Safe Operations - Prevents circular references and invalid moves
#Requirements
- PHP 8.2 or higher
- Laravel 11 or 12
- Filament 4.x or 5.x
#Installation
Install the package via Composer:
composer require openplain/filament-tree-viewPublish the package assets:
php artisan filament:assetsThat's it! The plugin registers its CSS and JavaScript assets with Filament automatically. Everything is now configured and ready to use.
#Quick Start
#1. Prepare Your Database
Create a migration with the required tree structure columns:
Schema::create('categories', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->boolean('is_active')->default(true); // Required for tree structure $table->foreignId('parent_id')->nullable()->constrained('categories'); $table->integer('order')->default(0); $table->timestamps();});#2. Add Trait to Your Model
Add the HasTreeStructure trait to enable tree functionality:
<?php namespace App\Models; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;use Openplain\FilamentTreeView\Concerns\HasTreeStructure; class Category extends Model{ use HasTreeStructure; protected $fillable = ['name', 'is_active', 'parent_id', 'order'];}The trait provides:
- Recursive parent/child relationships
- Automatic cascade delete for descendants
- Tree query helpers (roots, leaves, depth calculations)
#3. Add Tree Configuration to Your Resource
Add a tree() method to your resource alongside form() and table():
<?php namespace App\Filament\Resources; use App\Filament\Resources\CategoryResource\Pages;use App\Models\Category;use Filament\Resources\Resource;use Filament\Schemas\Schema;use Openplain\FilamentTreeView\Fields\IconField;use Openplain\FilamentTreeView\Fields\TextField;use Openplain\FilamentTreeView\Tree; class CategoryResource extends Resource{ protected static ?string $model = Category::class; public static function form(Schema $schema): Schema { // Your form configuration } public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree { return $tree ->fields([ TextField::make('name'), IconField::make('is_active'), ]); } public static function getPages(): array { return [ 'index' => Pages\TreeCategories::route('/'), 'create' => Pages\CreateCategory::route('/create'), 'edit' => Pages\EditCategory::route('/{record}/edit'), ]; }}#4. Create a Tree Page
Create a simple page that extends TreePage:
<?php namespace App\Filament\Resources\CategoryResource\Pages; use App\Filament\Resources\CategoryResource;use Openplain\FilamentTreeView\Resources\Pages\TreePage; class TreeCategories extends TreePage{ protected static string $resource = CategoryResource::class;}That's it! You now have a fully functional drag-and-drop tree view with manual save mode.
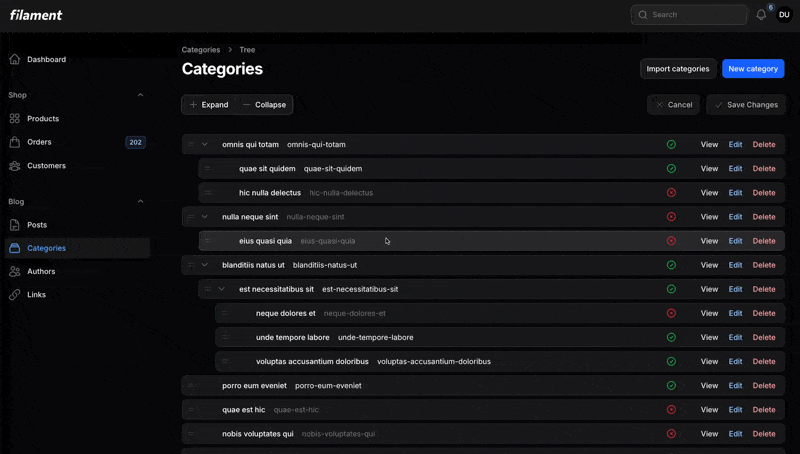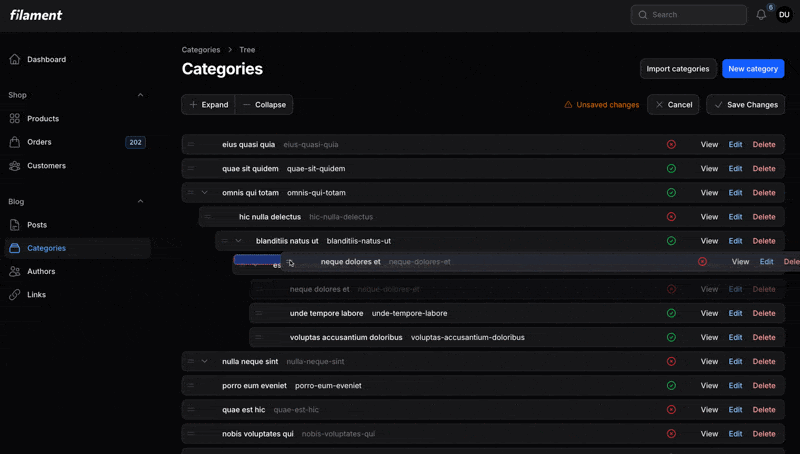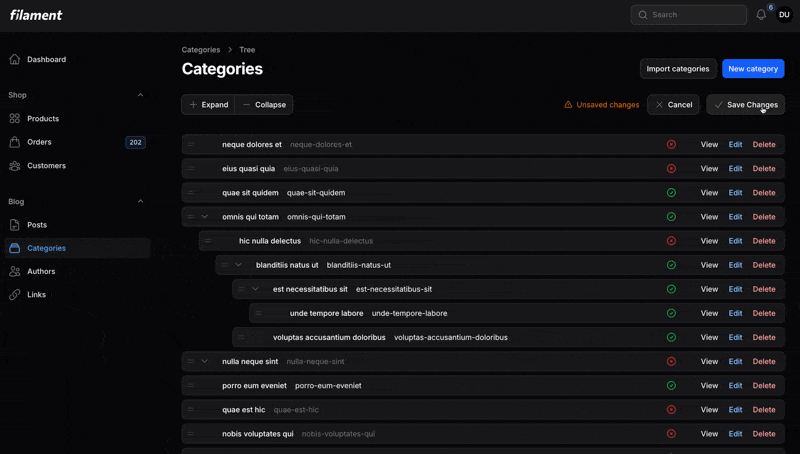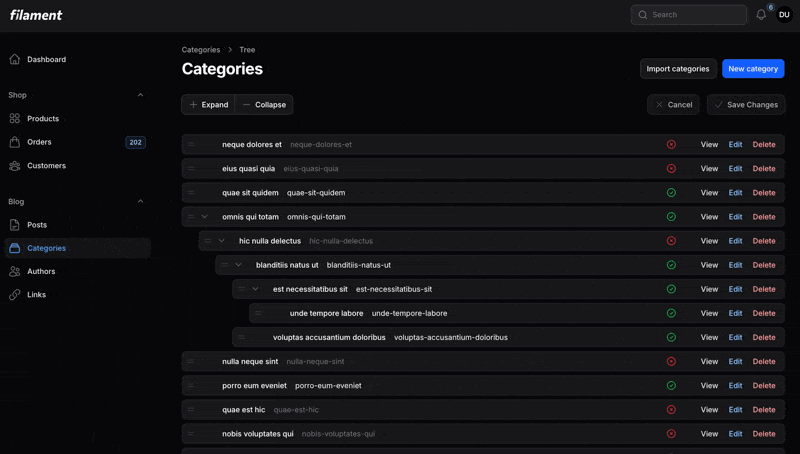
#Relation Pages
If you're using Filament's relation pages (extending ManageRelatedRecords), you can use TreeRelationPage instead of TreePage. This is ideal when you want to manage a hierarchical relationship separately from editing or viewing the owner record.
#When to Use TreeRelationPage
- You're using resource sub-navigation and want to switch between View/Edit pages and the relation page
- You want to keep relationship management separate from the owner record
- The tree configuration should come from the related resource, not the parent resource
#Example: Managing Category Children
<?php namespace App\Filament\Resources\CategoryResource\Pages; use App\Filament\Resources\CategoryResource;use Openplain\FilamentTreeView\Resources\Pages\TreeRelationPage; class ManageCategoryChildren extends TreeRelationPage{ protected static string $resource = CategoryResource::class; protected static string $relationship = 'children'; protected static ?string $relatedResource = CategoryResource::class;}Register the page in your resource:
public static function getPages(): array{ return [ 'index' => Pages\ListCategories::route('/'), 'create' => Pages\CreateCategory::route('/create'), 'view' => Pages\ViewCategory::route('/{record}'), 'edit' => Pages\EditCategory::route('/{record}/edit'), 'children' => Pages\ManageCategoryChildren::route('/{record}/children'), ];}#Advanced Configuration
Need more control? The tree view offers powerful customization options. All configuration is optional - only add what you need.
#Understanding Defaults
The tree uses sensible defaults for most settings:
- Fields: Required - You must configure which fields to display
- Actions: Optional - No actions shown unless you add them
- Collapse: Enabled by default - individual toggles + header Expand All/Collapse All buttons
- Save Mode: Manual save with Save/Cancel buttons (safer)
- Depth: 10 levels by default
Quick Links:
- Tree Behavior - Depth limits, collapse, auto-save
- Custom Fields - Display custom data in nodes
- Actions - Add edit, delete, and custom actions
- Model Configuration - Customize column names
- Empty State - Customize the "no records" view
- Save Behavior - Manual vs auto-save
- Query Customization - Filter and order records
#Tree Behavior
Control how your tree displays and behaves:
public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree{ return $tree ->maxDepth(5) // Limit nesting to 5 levels ->collapsed() // Start with nodes collapsed ->autoSave(); // Save immediately on reorder}Available Options:
| Method | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
maxDepth(int|null) |
10 levels | Restrict maximum tree depth (pass null for unlimited) |
collapsible(bool) |
Enabled | Individual toggles + header Expand All/Collapse All buttons |
collapsed() |
Expanded | Start with nodes collapsed instead of expanded |
autoSave() |
Disabled | Save changes immediately on drag-and-drop |
Common Patterns:
// Default - fully featured tree (collapsible, expanded, manual save)return $tree->fields([...]); // Simple/small tree - disable collapsereturn $tree ->fields([...]) ->collapsible(false); // Large tree - start collapsed for better performancereturn $tree ->fields([...]) ->collapsed(); // Auto-save for simple admin treesreturn $tree ->fields([...]) ->autoSave();#Custom Fields
Fields are required - you must configure which fields to display in your tree nodes.
Use the Field API to define what data appears in each tree node:
use Openplain\FilamentTreeView\Fields\TextField;use Openplain\FilamentTreeView\Fields\IconField;use Filament\Support\Enums\Alignment;use Filament\Support\Enums\FontWeight; public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree{ return $tree ->fields([ TextField::make('name') ->weight(FontWeight::Medium) ->dimWhenInactive(), TextField::make('description') ->color('gray') ->limit(50) ->dimWhenInactive(), IconField::make('is_active') ->alignEnd(), ]);}#TextField Options
TextField::make('name') // Typography ->size('sm' | 'base' | 'lg') ->weight(FontWeight::Thin | FontWeight::Medium | FontWeight::Bold) // Colors (Filament color names) ->color('primary' | 'gray' | 'success' | 'warning' | 'danger') // Alignment ->alignStart() // default ->alignCenter() ->alignEnd() // Content formatting ->limit(50) // Truncate with ellipsis ->formatStateUsing(fn (string $state): string => strtoupper($state)) // Conditional dimming ->dimWhenInactive() // Defaults to 'is_active' field ->dimWhenInactive('custom_status') // Or specify a custom field ->dimWhen('field_name', value: false); // Or check any field for any value#IconField Options
IconField::make('is_active') // Icons (Heroicon enum) ->trueIcon(Heroicon::OutlinedCheckCircle) ->falseIcon(Heroicon::OutlinedXCircle) // Colors ->trueColor('success') ->falseColor('danger') // Alignment ->alignEnd(); // Typically right-aligned#Actions
Add actions to tree nodes just like Filament Tables:
use Filament\Actions\EditAction;use Filament\Actions\DeleteAction;use Filament\Actions\Action; public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree{ return $tree ->recordActions([ // Navigate to edit page EditAction::make() ->url(fn (Category $record): string => static::getUrl('edit', ['record' => $record]) ), // Edit in modal Action::make('editModal') ->label('Quick Edit') ->icon('heroicon-o-pencil-square') ->fillForm(fn (Category $record): array => [ 'name' => $record->name, 'description' => $record->description, ]) ->form([ TextInput::make('name')->required(), Textarea::make('description'), ]) ->action(function (Category $record, array $data) { $record->update($data); Notification::make() ->title('Category updated') ->success() ->send(); }), // Delete with descendant warning DeleteAction::make() ->modalDescription(function (Category $record): string { $count = $record->descendants()->count(); if ($count === 0) { return 'Are you sure you want to delete this category?'; } return "This category has {$count} descendants that will also be deleted."; }), ]);}#Model Configuration
The HasTreeStructure trait uses sensible defaults, but you can customize column names for legacy databases:
class Category extends Model{ use HasTreeStructure; /** * Parent ID column name (default: 'parent_id') * * Override this for legacy databases with custom column names. * Common examples: 'parent_category_id', 'category_parent_id', 'parent' */ public function getParentKeyName(): string { return 'parent_category_id'; // Your legacy column name } /** * Primary key column name (default: 'id') */ public function getLocalKeyName(): string { return $this->getKeyName(); // Usually 'id' } /** * Virtual depth attribute (default: 'depth') * Calculated during queries, not stored */ public function getDepthName(): string { return 'depth'; } /** * Virtual path attribute (default: 'path') * Example: [1, 5, 12] = root(1) > parent(5) > current(12) * Calculated during queries, not stored */ public function getPathName(): string { return 'path'; } /** * Children relationship name (default: 'children') */ public function getChildrenKeyName(): string { return 'children'; } /** * Order column name (default: 'order') * Override this for legacy databases with custom column names. * Common examples: 'sort_order', 'position', 'sort', 'sequence' */ public function getOrderKeyName(): string { return 'sort_order'; // Your legacy column name } /** * Root parent value (default: null) * Override this for existing databases that use -1, 0, or other values * to represent root nodes (nodes without a parent) */ public function getParentKeyDefaultValue(): mixed { return null; // or -1, 0, etc. }}#Working with Existing Databases
#Custom Parent Field Name
If your legacy database uses a different column name for the parent relationship (instead of parent_id), override the getParentKeyName() method:
class Category extends Model{ use HasTreeStructure; /** * Your database uses 'parent_category_id' instead of 'parent_id' */ public function getParentKeyName(): string { return 'parent_category_id'; }}Common legacy field names:
parent_category_id- Category-specific parent fieldcategory_parent_id- Alternative naming conventionparent- Simplified field nameparent_node_id- Generic tree structure naming
No migration needed! The tree view will automatically use your custom field name for all queries and updates.
#Custom Order Field Name
If your legacy database uses a different column name for the sort order (instead of order), override the getOrderKeyName() method:
class Category extends Model{ use HasTreeStructure; /** * Your database uses 'sort_order' instead of 'order' */ public function getOrderKeyName(): string { return 'sort_order'; }}Common legacy field names:
sort_order- Common in legacy systemsposition- Alternative naming conventionsort- Simplified field namesequence- Alternative namingdisplay_order- Descriptive field name
No migration needed! The tree view will automatically use your custom field name for all ordering operations.
#Custom Root Parent Value
If your existing database uses -1, 0, or another value to represent root nodes instead of NULL, override the getParentKeyDefaultValue() method:
class Category extends Model{ use HasTreeStructure; /** * Existing database uses -1 for root nodes */ public function getParentKeyDefaultValue(): mixed { return -1; }}#Combining Multiple Customizations
You can override multiple methods for complete legacy database support:
class Category extends Model{ use HasTreeStructure; public function getParentKeyName(): string { return 'parent_category_id'; // Custom parent field name } public function getOrderKeyName(): string { return 'sort_order'; // Custom order field name } public function getParentKeyDefaultValue(): mixed { return -1; // Custom root value }}No database migrations needed! The package handles all queries and updates automatically.
#Customizing Empty State
public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree{ return $tree ->emptyStateHeading('No categories yet') ->emptyStateDescription('Get started by creating your first category.') ->emptyStateIcon('heroicon-o-rectangle-stack') ->emptyStateActions([ CreateAction::make() ->label('Create first category'), ]);}#Save Behavior
By default, the tree uses manual save mode - changes require clicking "Save Changes":
return $tree; // Manual save mode - safe defaultEnable auto-save to save immediately on every drag-and-drop:
return $tree->autoSave(); // Saves instantlyWhy manual save is the default:
- ✅ Review all changes before committing
- ✅ Cancel to discard unwanted changes
- ✅ Safer for production environments
- ✅ Better for complex hierarchies
When to use auto-save:
- Simple admin-only trees
- Single-user scenarios
- Immediate feedback preferred
#Query Customization
Modify the base query for your tree:
public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree{ return $tree ->modifyQueryUsing(fn (Builder $query) => $query ->where('status', 'active') ->orderBy('name') );}#Common Patterns
Real-world examples to help you get started quickly:
#Building a Navigation Menu
class MenuItem extends Model{ use HasTreeStructure; protected $fillable = ['label', 'url', 'icon', 'parent_id', 'order', 'is_active'];} public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree{ return $tree ->maxDepth(3) // Limit menu depth ->fields([ TextField::make('label')->weight(FontWeight::Medium), TextField::make('url')->color('gray'), TextField::make('icon')->color('gray'), IconField::make('is_active')->alignEnd(), ]) ->recordActions([ EditAction::make(), DeleteAction::make(), ]);}#Product Categories with Status
public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree{ return $tree ->fields([ TextField::make('name') ->weight(FontWeight::Medium) ->dimWhenInactive(), TextField::make('products_count') ->formatStateUsing(fn (int $state): string => "{$state} products") ->color('gray'), TextField::make('status') ->formatStateUsing(fn (string $state): string => ucfirst($state)) ->color(fn (string $state): string => match ($state) { 'published' => 'success', 'draft' => 'warning', default => 'gray', }), IconField::make('is_active')->alignEnd(), ]);}#Department Hierarchy
class Department extends Model{ use HasTreeStructure; public function employees() { return $this->hasMany(Employee::class); }} public static function tree(Tree $tree): Tree{ return $tree ->maxDepth(5) ->fields([ TextField::make('name')->weight(FontWeight::Bold), TextField::make('manager_name')->color('gray'), TextField::make('employees_count') ->formatStateUsing(fn (?int $state): string => $state ? "{$state} employees" : 'No employees' ) ->color('gray'), ]);}#Troubleshooting
#Styling Issues or Missing Styles
If the tree view appears unstyled or layouts look broken:
-
Republish assets:
php artisan filament:assets -
Clear browser cache - Hard refresh your browser (Cmd+Shift+R on Mac, Ctrl+Shift+R on Windows/Linux)
-
Clear application caches:
php artisan filament:cache-componentsphp artisan view:clear
#JavaScript Not Loading
If drag-and-drop doesn't work after installation:
# Publish assetsphp artisan filament:assets # Clear cachesphp artisan filament:cache-componentsphp artisan view:clear#Drag Restrictions
If you can't drag items to certain positions:
- Depth limit reached - Check your
maxDepth()setting - Circular reference - Can't move a parent into its own descendant
- Custom canDrop logic - Review any custom drop validation
#Performance with Large Trees
For trees with hundreds of nodes:
- Consider pagination or filtering at the root level
- Use
->collapsed()to start with nodes collapsed - Eager load relationships in
modifyQueryUsing()
->modifyQueryUsing(fn (Builder $query) => $query->with(['children', 'someRelation']))#ComponentNotFoundException After Creating TreePage
If you encounter Unable to find component: [app.filament.resources.blog.categories.pages.tree-categories] when clicking actions:
Cause: Laravel and Livewire cache component registries. New TreePage classes aren't immediately discoverable.
Fix:
composer dump-autoloadphp artisan optimize:clearThis clears Composer's autoloader, Livewire's component cache, and all Laravel caches. The error occurs after creating new TreePage classes or when updating the plugin in development environments.
#Testing
Run the test suite:
composer testRun Pint for code style:
composer pint#Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for details.
#Security
If you discover a security vulnerability, please email security@openplain.com. All security vulnerabilities will be promptly addressed.
#Credits
Built with these excellent open-source libraries:
- Laravel Adjacency List by Jonas Staudenmeir - Battle-tested recursive tree queries with thousands of production deployments
- Pragmatic Drag & Drop by Atlassian - Accessible, performant drag-and-drop used in Jira, Trello, and Confluence
#License
The MIT License (MIT). Please see License File for more information.
Built with ❤️ by Openplain

